In this article you will learn about bulking Of sand. It is also called as sand bulkage.
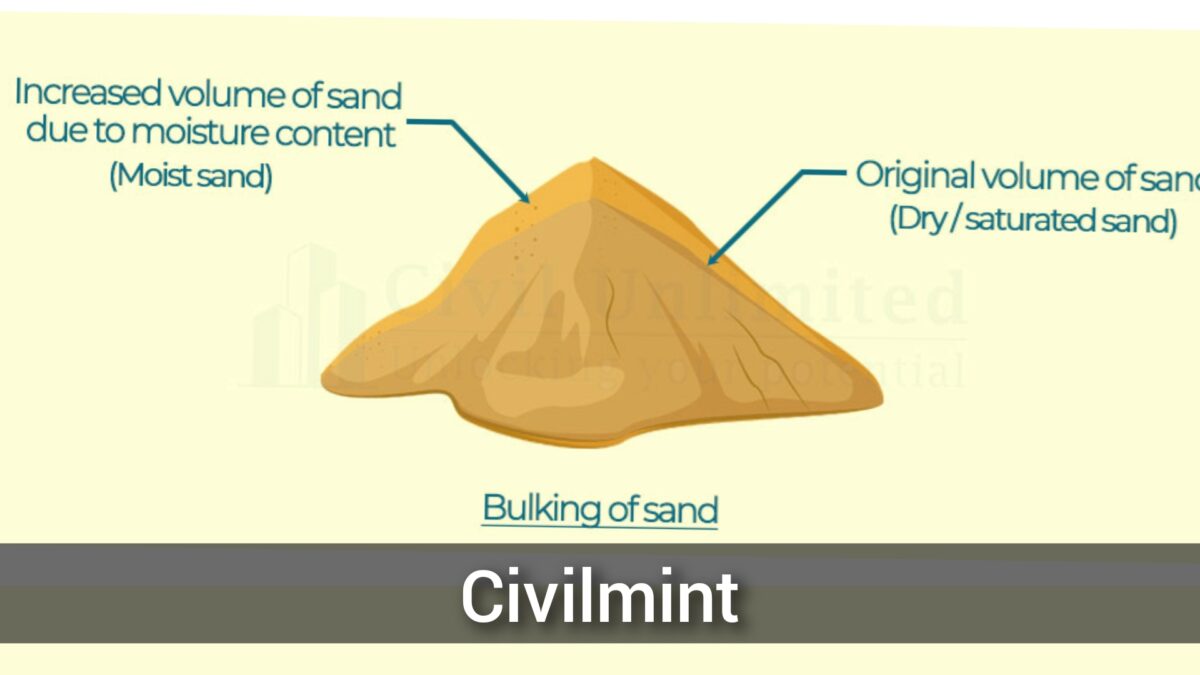
Table of Contents
What Is Bulking Of Sand?
When Sand contains moisture, the water forms a thin film around the sand particles. This increases the distance between the particles thereby increasing the volume of the Sand. This phenomenon is called the Bulking of Sand or Swelling of Sand.
From the above definition, we got some idea about Bulking of Sand. Right!
Now, let us take a deep dive to understand the whole process.
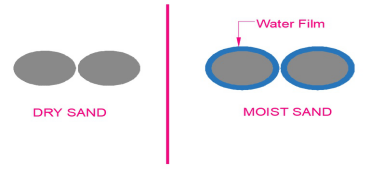
There are two particles of sand (left side) in a dry state and those particles are touching each other but now the same particles when the Sand is moist (right side) a film of water formed around the sand particles and get separated from each other.
What Is Bulk Density Of Sand?
The bulk density of sand is the weight of dry sand per unit of volume when it is in a loose, uncompressed state. Engineers and constructors use it to determine the amount of sand required to fill a given volume or to calculate the weight of sand needed for a particular project.
Several factors affect the bulk density of sand, including the particle size, shape, and gradation of the sand, as well as the degree of compaction and moisture content. Fine sand has a higher bulk density than coarse sand, and rounded sand has a higher bulk density than angular sand. Higher compaction and lower moisture content result in higher bulk densities.
Sand’s typical bulk density ranges from 1.4 to 1.6 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or 1400 to 1600 kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³), but it can vary depending on the specific type of sand and other environmental and physical factors.
Measuring the bulk density of sand involves using several methods. The sand replacement method involves digging a hole in the ground, filling it with sand, and then measuring the volume of sand used to fill the hole.
The core cutter method involves taking a cylindrical sample of sand, weighing it, and then measuring the volume of the sample. The water displacement method involves filling a container with water, adding a known amount of dry sand, and then measuring the volume of water displaced by the sand.
Various Causes Of Bulking Of Sand
1. Moisture content:
As mentioned earlier, moisture is the primary cause of bulking. When sand is dry, its particles are in close contact with each other, and the voids between them are minimal. But when water is added to the sand, the particles absorb the water and move away from each other, causing the volume to increase.
2. Particle shape and size:
The shape and size of sand particles also play a role in bulking. Angular particles tend to pack more tightly together, whereas rounded particles have more voids between them. Fine sand particles have a greater surface area and tend to absorb more water, causing more bulking than coarse sand particles.
3. Compaction:
The degree of compaction also affects the amount of bulking. If sand is compacted, there is less space for water to fill, and therefore less bulking will occur. Conversely, loose sand will have more voids, allowing more water to fill, causing more bulking.
4. Presence of impurities:
The presence of impurities such as clay or silt in the sand can also contribute to bulking. These impurities tend to absorb more water than pure sand, leading to more significant bulking.
What Percentage Of Moisture Causes Bulking In The Sand?
Bulking occurs only for very specific water content in the sand.
Bulking of Sand occurs when moisture is present from 5% to 8% which causes an increase in the volume ranging from 20% to 30%.
What Happens When Moisture Increases Beyond 8%?
More moisture beyond this reduces the Bulking of Sand and in the fully saturated state the film around the sand particles disappears and the volume of sand is equal to its dry volume.
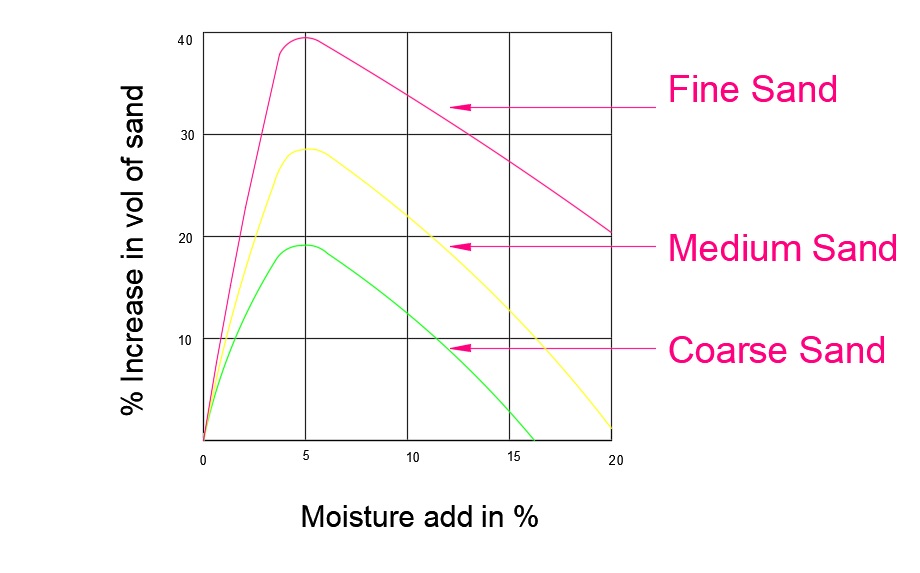
There is a very small range (5 to 8 %) in which the bulking occurs. Beyond 8% volume again starts reducing to its original volume (see figure ).
In the graph, there are three types of sand, Fine Sand, Medium Sand, and Coarse Sand. From the graph, it is quite obvious that the Bulking is maximum for Fine Sand and then for Medium Sand and least for the Coarse Sand.
In the case of Fine Sand, the number of particles is more hence the increase in volume will also be more.
Consequence Of Bulking
When preparing concrete/mortar by the volumetric method using bulked sand, the actual sand added in the mix is less than if it was in the dry state. This leads to the sand deficient concrete/mortar.
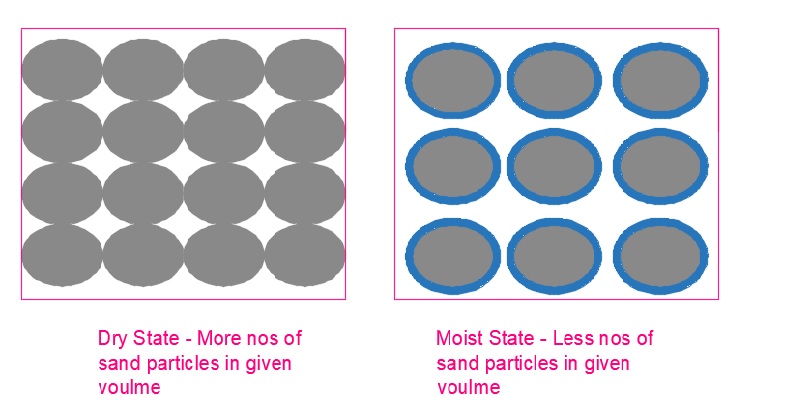
From the above figure, for a given volume more numbers of sand particles in dry sate but in the same volume fewer numbers of sand particles in the moist state because the volume is occupied by the film of water.
Solution If The Sand is Bulked
Additional sand needs to be added to compensate for the deficiency. The water present in the sand needs to be considered when calculating the water-cement ratio.
How To Determine The Percentage Of Bulking By Laboratory Test
Laboratory Test for Bulking Of Sand
The amount of bulking of sand can be easily determined by a simple test as follows.
The moist sand sample is taken in a measuring cylinder and its volume is noted. The measuring cylinder is then filled with water so that the sand is completely saturated.
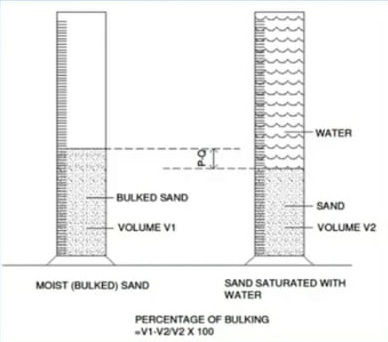
The cylinder is shaken and the sand is allowed to settle. The volume of the settled sand is noted. The difference in the percentage of volume in the moist condition and saturated condition indicates the percentage of bulking. If V1 is the volume of moist sand and V2 is the volume of saturated sand then the percentage difference is calculated by the formula as follows
Percentage of Bulking = (V1-V2)/V2*100
If this percentage of bulking is within the range of 5 to 8 % we will say that sand has bulked and in that case, we will add extra sand in the mix to compensate for bulking.
Faqs
Bulkage of sand occurs when the presence of air voids between the particles causes an increase in volume of the sand, which is also known as bulking of sand.
Sand bulks due to the presence of air voids between the particles. When sand is dry, the voids between the particles are filled with air, which causes the sand to increase in volume and decrease in weight.
Bulkage affects the quantity of sand required for a construction project by increasing the volume of the sand. If the increase in volume is not taken into account, the actual quantity of sand required will be underestimated, leading to project delays and cost overruns.
To measure the bulkage of sand, the volume of a given weight of sand in its loose state is compared to its compacted state. The difference in volume between the two states is the bulkage factor.
Yes, the bulkage factor of sand can vary depending on the source of the sand due to factors such as the shape and size of the sand particles, moisture content, and the presence of impurities. Therefore, it is important to test the bulkage factor of sand from each source to ensure accurate calculations.
