Table of Contents
What is a Flat Slab?
A reinforced concrete slab supported directly by concrete columns without the use of beams is known as a flat slab. The term “flat-slab” refers to a one- or two-sided support system with the slab’s shear stress concentrated on the supporting columns and a square slab known as “drop panels.”
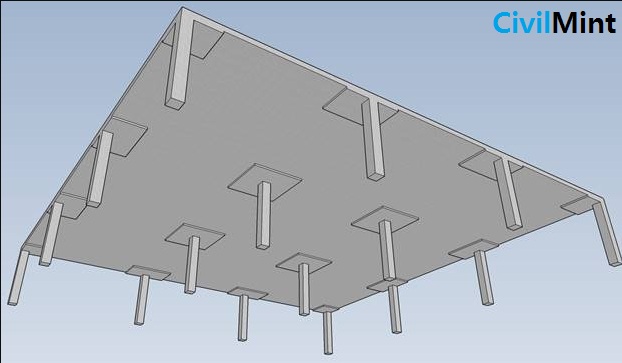
Drop panels are important because they increase the overall capacity and durability of the flooring system beneath the vertical loads, consequently increasing the construction’s cost-effectiveness. Drop panels are usually around two times the height of the slab.
Flat Slabs are suited for most types of construction as well as asymmetrical column layouts such as curving floors and ramps. There are multiple advantages to using flat slabs, including depth solution, level soffit, and design arrangement freedom.
Even though flat slab construction can be costly, it provides architects and engineers with a great deal of architectural freedom.
The advantages of choosing flat slabs are not only in terms of potential design and layout efficacy but also in terms of the whole construction process, particularly in terms of facilitating installation processes and reducing construction time.
If at all feasible, using drop panels much be avoided as much as possible and make the most of the thickness of flat slabs. To maintain the benefits of flat soffits for the floor surface, make sure that drop panels are cast as part of the column.
The following are the most important considerations to keep in mind when optimizing slab thickness:
- Design-related procedure
- Holes’ presence or absence
- The significance of deflections
- Experience with application of the previous layout
Types of Flat Slabs
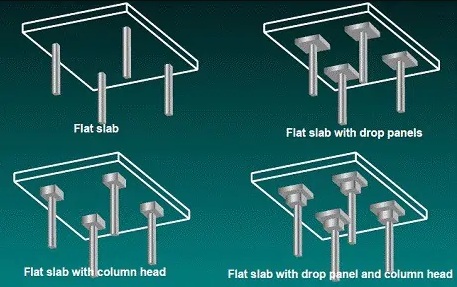
The varieties of flab slab construction are as follows:
- Simple flat slab
- Flat slab with drop panels
- Flat slab with column heads
- Flat slab with both drop panels and column heads
Uses of Column Heads
- It boosts the slab’s shear resistance.
- Reducing the clear or effective span lowers the moment in the slab.
Uses of Drop Panels
- It increases the slab’s shear resistance.
- It enhances the slab’s ability to withstand negative forces.
- It reduces deflection by stiffening the slab.
Advantages of Flat Slab
It has been observed that flat slabs without drop panels can be built quickly because the structure’s framework is simpler and reduced. A system that uses early striking and flying systems can also be used to achieve a quick turnaround.
Flat slab construction can significantly reduce floor-to-floor height, especially in the absence of a false ceiling, because it restricts the placement of horizontal services and partitions. This can be advantageous in cases of reduced building height, lower cladding costs, and prefabricated services.
If the client wishes to make adjustments to the interior and use the space as needed, flat slab construction is the best option because it gives the owner that flexibility. Due to the use of a square lattice and the lack of a beam, which makes service channeling and partition allocation difficult, this flexibility is available.
The thickness of the flat slab
The thickness of the flat slab is another appealing feature, as it allows for more floor-to-ceiling height and cheaper cladding costs for the owner. However, because additional reinforcements are required to address design concerns, there is a significantly lower limit to slab thickness. Furthermore, additional margin must be provided to allow for architectural changes at a later date.
Types of Flat Slab Design
In creating flat slabs and analyzing these slabs in flexures, a number of processes and methodologies are used. The following are a few of these methods:
- The empirical method
- The sub-frame method
- The yield line method
- Finite–element analysis
Areas That Require Attention in the Design of Flat Slabs
1. Deflections:
The maximum deflections are usually found at the center of each panel. Predicting deflections is difficult and will necessitate some type of elastic evaluation. One strategy to analyze mid-panel deflection while building structural architecture and implementing the subframe method is to employ at least two parallel column strips.
2. Punching shear reinforcement systems:
Punching shear reinforcements are necessary in the case of thin flat slab construction.
3. Reinforcement Optimization:
Certain design procedures, particularly yield line output, are better optimized than other design methods.
Benefits of Using Flat Slab Construction Method
- Flexibility in room layout.
- Saving on building height.
- Shorter construction time.
- Single soffit level.
- Ease of installation of M&E services.
- Use of prefabricated welded mesh.
- Buildable score.
