Table of Contents
What Is Low Heat Cement?
Low heat cement is a special kind of cement that does not get very hot when it becomes hard. It is made differently from regular cement so that it doesn’t release too much heat.

Regular cement like portland cement can sometimes make things too hot when it hardens, which can be a problem for big buildings. But low heat cement is made to produce less heat, so it’s better for building large structures.
Low heat cement is made with different ingredients than regular cement. Some special things are added to it, like gypsum, fly ash, and slag, which help it stay cooler when it hardens.
Low heat cement has some really good qualities. It is stronger and lasts longer than regular cement. It also helps prevent cracks in big buildings. That is why people use it to build things like dams, nuclear power plants, and big walls.
Using low heat cement is good because it keeps the structures from getting too hot and getting damaged. It also helps the buildings stay strong and last a long time.
Composition Of Low Heat Cement
1. Portland cement clinker:
Low heat cement is mainly made from a substance called Portland cement clinker. To produce this, limestone and clay are heated at a high temperature in a kiln. The resulting material is then ground to create the clinker.
2. Gypsum:
Gypsum is added to low heat cement to control how quickly it sets and to make it easier to work with. It acts as a retarder, which means it slows down the process of the cement hardening.
3. Fly ash or slag:
Fly ash and slag are materials that can be added to the cement mixture to improve its properties and reduce heat generation. Fly ash is a fine powder that comes from coal-fired power plants, while slag is obtained from the production of iron and steel.
4. Calcium sulfate:
In addition to gypsum, other compounds of calcium sulfate may be added to low heat cement. These compounds help control the setting time of the cement and improve its performance.
5. Additives:
Low heat cement may contain specific chemical additives to further reduce heat generation during the hardening process. These additives can include substances like lignosulfonates, which make the cement easier to work with by reducing the amount of water needed. Manufacturers may also include their own proprietary additives to enhance the cement’s properties.
Characteristics Of Low Heat Cement
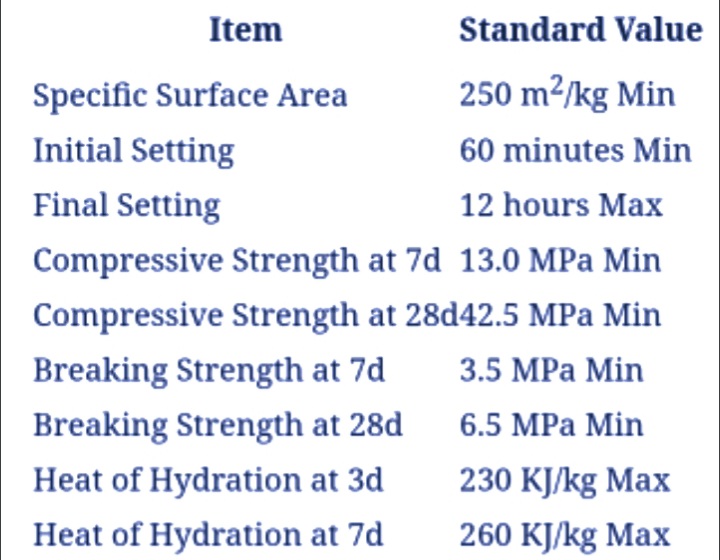
In the below figure, I have listed various properties of low heat cement.
Uses Of Low Heat Cement
Low heat cement is extensively utilized in the construction of large-scale concrete structures, such as dams, bridges, and foundations. These projects involve the pouring of substantial volumes of concrete, which can result in significant heat generation during the hydration process. Excessive heat can lead to thermal cracking, compromising the structural integrity of the construction. Low heat cement offers a solution by reducing the amount of heat generated, ensuring uniform hydration, and minimizing the risk of thermal stresses. Its application in mass concrete construction helps maintain the durability and longevity of the structures.
Low heat cement is highly advantageous in the construction of high-rise buildings. Tall structures require multiple concrete pours for each floor, and the heat generated during hydration can accumulate, leading to thermal differentials and potential structural issues. By incorporating low heat cement, construction teams can effectively manage the heat released and maintain precise temperature control. This allows the concrete to set properly, reducing the likelihood of cracking or other complications associated with excessive heat generation. The use of low heat cement in high-rise buildings ensures the structural integrity and stability of the construction.
Low heat cement finds particular importance in regions characterized by hot climates. In such areas, high ambient temperatures, coupled with the heat of hydration, can accelerate the setting process, making it challenging to work with concrete effectively. By utilizing low heat cement, construction projects can overcome this challenge and maintain extended workability. The reduced heat generation during hydration enables proper curing, avoiding premature stiffening and ensuring the development of stronger and more durable structures. Low heat cement is a valuable asset for infrastructure development in hot climates, enabling the construction of reliable and long-lasting concrete structures.
Advantages Of Low Heat Cement
- Low heat cement assists in minimizing the potential for thermal cracking in thick concrete sections.
- It offers improvised durability performance compared to ordinary Portland cement (OPC).
- Low heat cement exhibits excellent performances, including high final strength, sulphate corrosion resistance, good lasting properties, good resistance to rupture, and anti-seepage properties.
- It provides increased workability and pumpability, making it suitable for large pours in hydraulic engineering concrete and marine concrete works.
- Low heat cement shows significantly improved later-age concrete strengths.
- It is resistant to sulphate attack on reinforcement, particularly in concrete pipes.
Disadvantages Of Low Heat Cement
- The initial strength gained by low heat cement is lower compared to OPC concrete. However, the final strength is the same as that of OPC.
- This cement cannot be used in cold weather conditions due to its specific characteristics.
- The cost of low heat cement is higher than that of ordinary cement.
Faqs
Low heat cement generates less heat during curing due to its specific combination of raw materials and manufacturing processes.
Low heat cement helps prevent thermal cracking in concrete structures by minimizing the heat of hydration, which reduces the temperature rise during the curing process.
Yes, low heat cement can be used in small-scale construction projects where controlling the temperature rise is important, such as in residential buildings or smaller concrete structures.
No, there is no noticeable difference in the appearance or texture of low heat cement compared to regular cement. It looks and feels the same as regular cement.
Special precautions when using low heat cement include ensuring proper mixing, following recommended curing methods, and allowing for a longer setting time compared to regular cement. It is important to consult with professionals or experts to ensure proper usage.
