Reciprocating compressors are a well-known type of compressor in the positive displacement compressor category. Reciprocating compressors use pistons or plungers to compress air or gas. The back and forth movement of the piston compresses gas and air. Therefore, it is also called a piston compressor.
In this compressor, gas or air is drawn into the chamber where the reciprocating piston compresses. This piston works by moving the amount of hydraulic fluid.
The piston compressor is located where low gas flow and high pressure are required. These compressors are mainly used for inflating vehicle tires, small painting work, commercial applications, dust cleaning, hand tools, etc.

A reciprocating compressor is a unique device because it has an active element that can move in both linear and rotational directions. Therefore, you do not have to follow the basic rules of “vibration monitoring”, you can extend the life just by monitoring the operating condition of the compressor.
The main difference between the reciprocating compressor and the centrifugal compressor is that the reciprocating compressor uses a piston instead of a diffuser to compress the air.
Table of Contents
How Does Reciprocating Compressor Works?
The operating principle of the piston compressor is very simple. Powered by a gasoline/diesel engine or an electric motor.
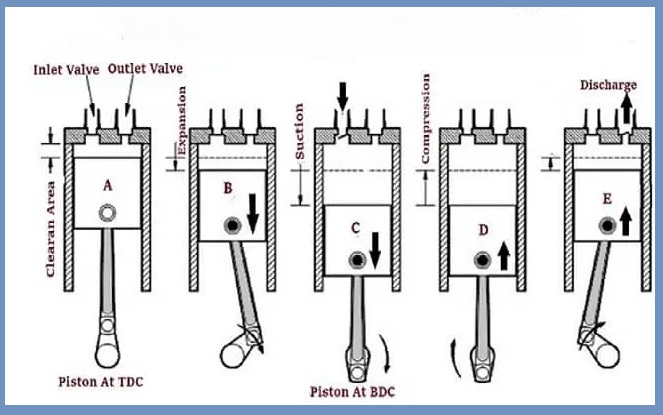
The piston compressor works as follows:
- When the switch is turned on, the electric motor begins to rotate and the shaft connected to the piston rotates.
- As the shaft rotates, the piston in the cylinder also begins to move in the CLOSE and FRO directions.
- As the piston of the reciprocating compressor moves toward the bottom dead center, the air pressure inside the cylinder becomes lower than the external pressure.
- Due to the low air pressure inside the cylinder, high pressure outside air begins to flow into the compressor cylinder.
- In this way, air begins to be drawn into the compressor cylinder through the intake valve.
- When the BDC cycle is complete, the piston begins an upstroke and begins to move towards the TDC.
- As the piston rises, the volume of the cylinder begins to decrease and the pressure in the inside air becomes equal to the pressure in the outside air or outside air. The suction valve closes during this process.
- During the TDC cycle, the piston compresses the air or gas in the cylinder. When the TDC cycle is complete, the release valve opens and the air is released to the desired location or storage location.
- After releasing air or gas, the entire cycle is repeated many times.
Types of Reciprocating Air Compressor
- According to the working of the piston
- According to the number of cylinders
1. According to the working of the piston
Depending on the function of the piston, the piston air compressor can be divided into two types.
- (i) Single Acting Compressor
- (ii) Double Acting Piston Air Compressor
2. According to the number of cylinders
- (i) Single Stage Air Compressor
- (ii) Two-Stage Compressor
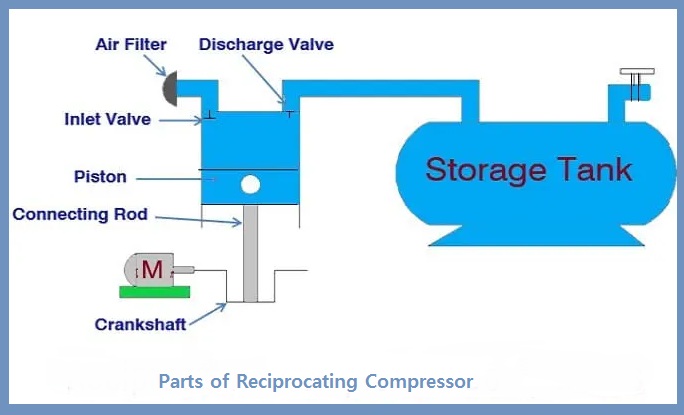
Parts of Reciprocating Compressor
Details of the key components of the piston compressor are given in the below image:
Pros:
- It is reasonably priced in comparison to different kinds of compressors.
- Easy to maintain.
- It is ideal for excessive-strain requirements.
- It is bendy to use.
- The reciprocating compressor has excessive efficiency.
Cons:
- These machines are heavy and large in size, which is a major problem.
- The noise level is very high.
- The outlet temperature of compressed air is very high.
Uses of Reciprocating Compressor
- Used in the refrigerator.
- These compressors are used in gas distribution systems.
- Use of piston compressors in oil refineries.
- Use in chemical plants.
