The radiator is part of the cooling system used to remove heat from the engine. The radiator is an important component of the vehicle that acts as a heat exchanger and transfers heat from the engine cooling water flowing through the radiator to the air blown by the fan. The main function of the radiator for cars is to prevent the engine from overheating and to cool the engine’s cooling water properly. Overheating of the engine or improper valve timing can cause serious damage to the vehicle.
Radiators are used to heat the environment and cool inflow fluids (that is, coolants) such as HVAC dry cooling towers and car engine cooling. The largest radiator transfers most of the heat by a convection process rather than heat radiation. They are a good source of heat for the environment.
The cooler is most commonly used in the automotive industry to cool the internal combustion engine of an automobile. They are also used in stationary power plants, motorcycles, locomotives, trains, piston-engine aircraft, and other applications where internal combustion engines are used.
Brass and copper are most commonly used in radiator construction due to their high thermal conductivity. The various parts of the radiator are almost completely soldered.
Table of Contents
How Does a Radiator Work?
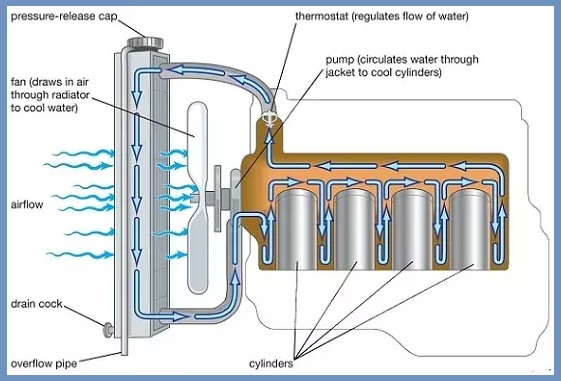
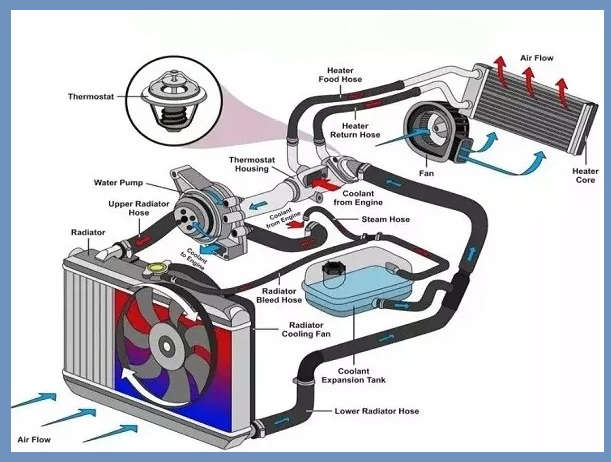
The radiator is one of the most important components of the engine cooling system. Helps maintain engine temperature. It is connected to the engine via a hose. Coolant flows through the hose.
The thermostat is mounted on the front of the radiator, which acts as a valve. It opens and closes according to the engine temperature. Adjust the flow of coolant.
The running of the radiator could be very simple. It works withinside the following way:
- When the engine temperature rises, the thermostat sends a signal to the water pump. The water pump is activated to pump the coolant into the hose. In the hose, the coolant circulates in the engine and absorbs its heat.
- When the coolant absorbs the heat of the engine, it gets hot. This hot coolant is sent to the radiator. This hot coolant enters the radiator through the inlet port. The radiator has a fan that forces cold air through the hot coolant. This air absorbs the coolant temperature and cools it.
- This cold coolant is sent back to the engine and the whole process is repeated.
- In this process, the radiator uses thin metal fins. These fins allow the heat of the coolant to be quickly dissipated to the air outside the vehicle.
Various Types of Radiators
- Tubular Type Core
- Cellular Type Core
1. Tubular Type Core
This type of cooler has two tanks, a lower tank, and an upper tank. These two tanks are interconnected by several pipes. Water or coolant flows through these pipes.
The tubular heater contains multiple fins mounted around the tube to increase the heat transfer coefficient. Air flows between the fins and the tube. This air absorbs heat from the water flowing through the pipe.
If any of these tubes become clogged, the cooling effect of that tube will be completely lost. However, with cell radiators, a single tube can be clogged with loss, but only a small portion of the entire cooling surface is affected.

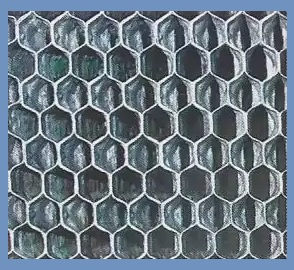
2. Cellular Type Core
The cellular core is also called a honeycomb radiator because of its design. In a cell radiator, water flows outside the tube and air flows inside the tube.
The core consists of a series of individual air cells. These cells are surrounded by water.
In the cell core, clogging of a single tube causes loss, but it affects only a small part of the entire cooling surface.
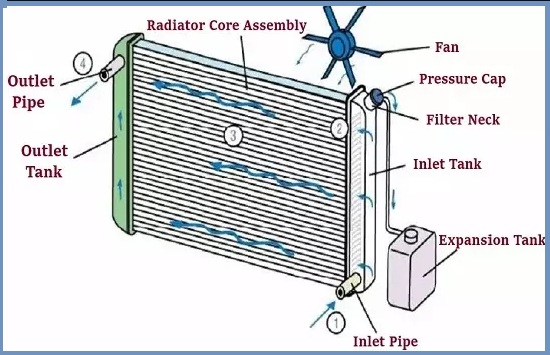
Components/Parts of Radiator
- Core
- Pressure Cap
- Inlet and outlet tanks
- Radiator Hoses
- Thermostat
- Water Pump
For better understanding, I also attached an image. See the below image.
Pros
- The radiator is very important to properly cool the engine.
- It prevents the engine from overheating. The heater is very efficient.
- They create very little pollution.
- These are environmentally friendly substances.
- Good performance of anti-oxidation and anti-corrosion
- Casting the radiator is very easy. Therefore, they are available in several models.
- Installing the radiator is very easy.
Cons
- The radiator has a high operating noise.
- Inadequate car radiator maintenance can lead to engine overheating.
- They need proper maintenance and care to work effectively.
- It requires a sufficient amount of air and coolant to operate effectively.
- The heat from the appliance involves sitting around the appliance, reducing living comfort, and creating drafts and cold spots. It can get very hot during operation. Keep infants or pets away from heaters in use.
Uses
- Radiators are most commonly used in vehicle cooling systems to cool the engine.
- They are used in the HVAC system.
- They are used for automatic transmission fluid cooling.
