In this article, we will learn about the direct injection fuel system. As the name suggests, In this system, fuel is ejected directly above the piston into the engine combustion chamber.
PDI (petrol-directed injection) is also known as GDI (gasoline direct injection).
This is a system to create an air-fuel mixture for gasoline-powered internal combustion engines. This system injects fuel directly into the engine’s combustion chamber.
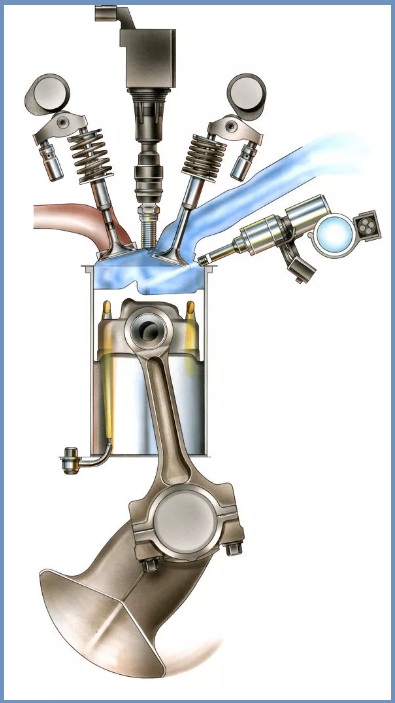
Direct injection systems are most often used in gasoline engines, but advances in technology have made them successful in diesel engines. These systems are used in gasoline engines to reduce emissions and increase specific output and engine efficiency.
In 1925, a gasoline direct injection engine was developed for low compression truck engines. In the 1950s, some German cars also began using Bosch’s mechanical GDI system. This technology became more and more popular when Mitsubishi introduced the electronic GDI system to production vehicles in 1996.
In recent years, many automotive industries have begun to use this technology. The direct injection principle was first implemented in diesel engines. Direct injection systems are mainly used in diesel engines. In a basic diesel engine, fuel is ejected directly into the combustion chamber above the piston.
In a diesel engine, a reciprocating piston in the combustion chamber compresses the air, ensuring temperatures above 400 degrees Celsius. Because the air is completely compressed, the direct injection system injects diesel fuel into the combustion chamber immediately. This fuel injection technology allows gasoline engines to burn fuel more efficiently with lower emission rates, resulting in higher power output, improved engine performance, and improved fuel efficiency.
Table of Contents
How Does Direct Injection Fuel System Work?
The working process of direct injection could be very simple. Petrol engines paintings by introducing a combination of petrol and air into the compression cylinder. This cylinder has a shifting piston to compress the combination to the preferred level. When the combination is compressed, a spark plug releases an electrical spark to provoke combustion. The strength generated through the air-gas combination moves the piston down and creates a force.
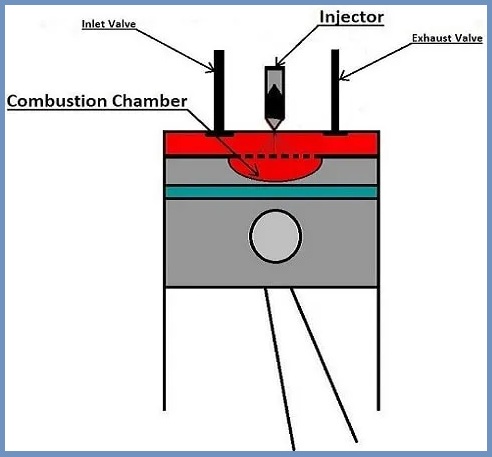
The direct injection system has a simple operation. Normally, in an indirect fuel injection system, the air and gasoline are pre-mixed in a cylinder outside the combustion chamber called the intake manifold. In this type of system, gasoline and air do not mix. In this system, fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber while air is introduced through the intake manifold. In the combustion chamber, the process of mixing air and fuel occurs.
Key Functions of Direct Injection Fuel System
- Reduce emission rate.
- It increases fuel consumption.
- Helps the engine generate more power
- Improves engine performance.
- Burn fuel efficiently.
Pros and Cons of Direct Injection Fuel System
Pros
- These systems process fuel at significantly higher pressures than indirect injection systems.
- It increases the power of the engine.
- Reduces engine emissions.
- This system extends engine life.
- High torque at low speeds.
- Direct injection engines require little maintenance.
Cons
- Direct injection systems for engines are expensive and complex to design.
- When plaque builds up in the arteries, blood flow to the heart is reduced, causing a heart attack. Carbon accumulation works in the same way. Accumulation of carbon in the intake valves of a car reduces the fuel supply to the engine, which can lead to engine damage or failure.
- The main drawback of direct injection systems is that direct injection can clog the fuel system and cause carbon deposits in the engine. This carbon accumulates in the intake valve.
