A piston is a reciprocating mechanical disc that reciprocates back and forth within the compression chamber of an engine. The movement is transmitted to the crankshaft via the connecting rod. The performance of the internal combustion engine depends on the operation of the piston.

This part of the internal combustion engine has metal moving part with a piston ring. The piston pin connects the connecting rod to the piston. This connecting rod is also connected to the crankshaft via a crankpin.
When the liquid or gas in the compression chamber contracts or expands, the piston disk in the chamber begins to move. Chemical energy is generated during the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture.
When the burned air-fuel mixture expands, the energy generated produces thrust. This thrust causes the piston to move back and forth. It transmits that movement to the crankshaft, which keeps the vehicle moving.
The piston needs to be reliable and flexible, but its weight should be as light as possible. Lightweight pistons help reduce the inertia created by their reciprocating mass.
Must be able to withstand the high explosive power and temperature generated in the compression chamber. The engine piston should move back and forth in the compression chamber with minimal friction.
Table of Contents
Role of Piston in an Engine
The main function of the piston is to compress only the air or air-fuel mixture in the cylinder and obtain energy from the burned air-fuel mixture. It absorbs the thrust generated by the burned air-fuel mixture in the cylinder and passes it to the connecting rod. Reciprocating in the combustion chamber. Performs suction, compression, expansion, and exhaust strokes. After completing these strokes, the crankshaft will rotate and the crankshaft will continue to rotate the vehicle’s wheels.
How Does a Piston Work?
The piston is a reciprocating part of the engine. Move back and forth in the combustion chamber or compression cylinder. Its reciprocating motion produces energy from the air-fuel mixture and helps rotate the wheels of the vehicle.
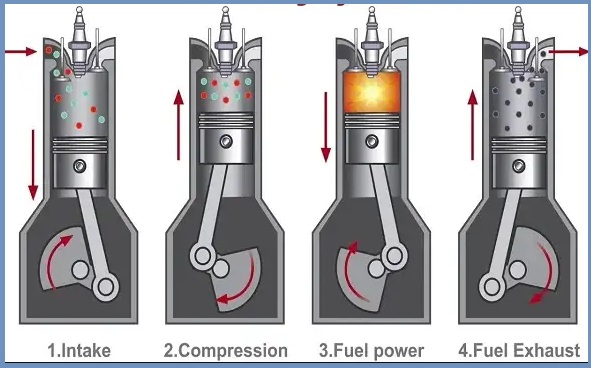
A piston works withinside the following way:
- For the suction stroke, the piston actions from TDC to BDC. During this movement, it generates a vacuum withinside the combustion chamber. A vacuum generates because it reaches BDC, which opens the suction valve. As the suction valve opens, the air-gasoline combination is delivered from the carburetor to the combustion chamber.
- After the suction stroke, the piston plays a compression stroke. For this stroke, it actions from BDC to TDC. During this movement, it reduces the quantity of the combustion chamber.
- As the combustion chamber quantity reduces, the air-gasoline combination compression occurs. As the piston reaches TDC, the air-gasoline combination is completely compressed.
- A spark plug ignites the combination while the combination is completely compressed in keeping with the requirements. Due to the ignition of the air-gasoline combination, warmth strength is produced withinside the combustion chamber.
- As the combusted air gasoline passes thru a growth valve, it expands and forces the piston to transport from TDC to BDC.
- When the piston receives electricity through an accelerated air-gasoline combination, it reciprocates and similarly reciprocates the connecting rod. The connecting rod, in conjunction with the crankpin, converts the reciprocating movement into rotary movement and provides it to the crankshaft. The crankshaft similarly provides rotary movement to the flywheel, which turns the automobile wheels.
- In the final, the piston plays the exhaust stroke. For this stroke, the piston once more actions from BDC to TDC and expels the exhaust gases out of the combustion chamber. After this final stroke, the entire cycle repeats.
Diffrent Types of Pistons
- Trunk Pistons
- Crosshead Pistons
- Sliding piston
- Deflector Pistons
- Racing pistons
- Invar strut piston
- Autothermic Pistons
- Specialliod Pistons
Key Uses of Pistons
- Pistons are maximum typically utilized in engines to compress the air-gasoline mixture.
- It is reciprocating a part of the engine. It is likewise utilized in
- piston pumps. Pump cylinder piston. Their principal reason is to boom the strain of the liquid and pump it to the favored area.
- These are utilized in compressors to compress fuel lines or air.
