Table of Contents
Specific Gravity Of Cement:
The weight of the volume of cement to the weight of the volume of water is known as the specific gravity of cement. Normally, it varies from 3.1 to 3.16 g/cc.
Specific Gravity of Cement = (weight of the volume of cement/weight of the volume of water)
Specific Gravity Test of Cement:
The specific gravity of cement is determined by Le Chatelier’s Flask method. This test is also known as the Cement density test.
Specific Gravity Test Apparatus:
The following apparatus is required for the Cement density test.
- Cement
- Kerosene
- Specific Gravity Bottle capacity of 250 ml with stopper.
- Weighing balance with 0.1 gm accurate
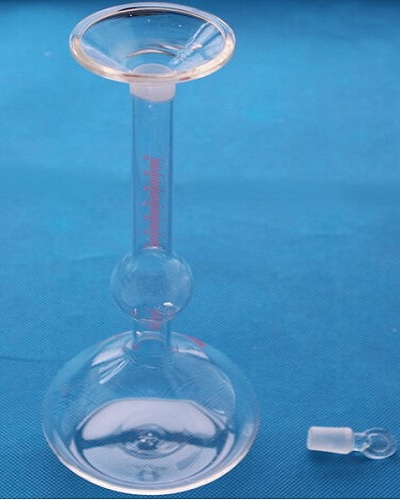

Test Procedure to Find Specific Gravity of Cement:
- First, make sure that the Lechatlier flask is free from moisture.
- Calculate the weight of the vacant flask and noted it as W1.
- Take a 50-gram cement sample and add it to the flask. Now measure the weight of the flask with the stopper as W2.
- Now pour kerosene oil in the cement sample up to the neck of the bottle. Mix thoroughly and make sure that there should be no air bubbles left in the flask. Consider it as W3.
- Empty the flask and fill the bottle with kerosene oil up to the tip of the bottle and consider it as a W4.
The specific gravity of the cement can be calculated from the following formula.
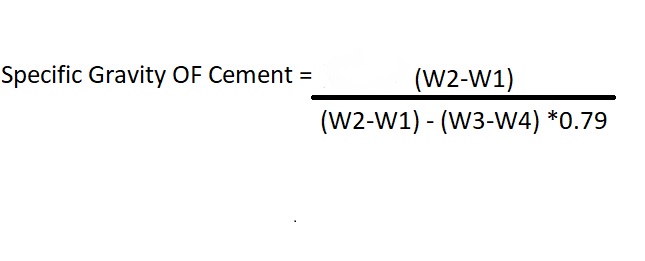
Where Specific gravity of Kerosene = 0.79 g/cc.
The specific gravity of a good quality cement should vary from 3.1 to 3.6 g/cc.
